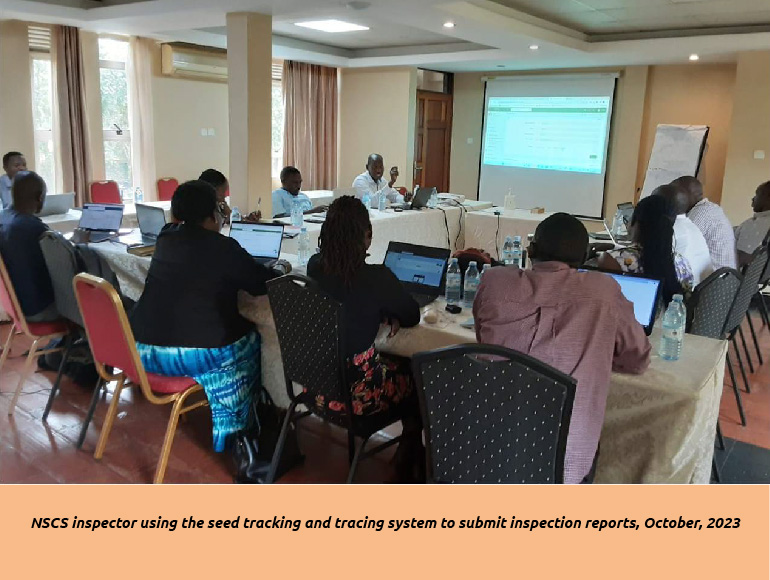
Digitizing the seed sector of Uganda: The Seed tracking and tracing system, STTS innovation.
Ugandan farmers continue to face challenges of accessing quality seed in the market as about 40% of seed in the market is reported be counterfeit (National Seed Policy, 2018). This challenge is exacerbated by effect of climate change resulting into persistent low yields and crop failure in many cases. Despite its effect on low productivity and crop failure, counterfeit seed limits smallholder farmers’ ability to effectively to adapt to the adverse effect of climate change. Crop breeders developed many crop species tolerant to biotic and abiotic stress caused by effects of climate change. However, farmers do not receive these agricultural technologies as most farmers end up buying fake products in the market due to counterfeiting. Through quality seed, a state-of-the art technology can reach farmers and that can account for higher yields, disease and pests resistance, climate change adaption, reduced post-harvest losses, and improved nutrition is critical in improving food and nutrition security across Africa and in particular in Uganda (TASAI Uganda Country Report, 2021).
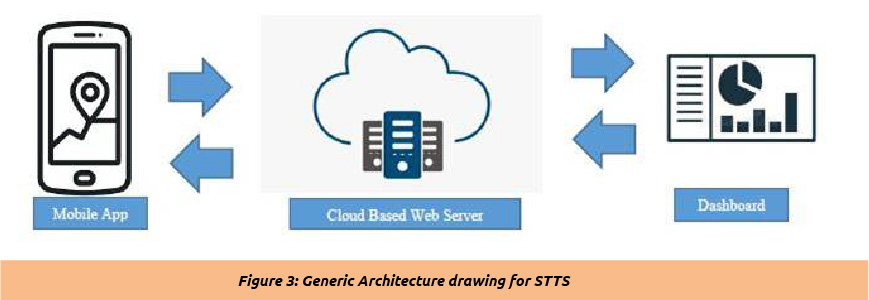
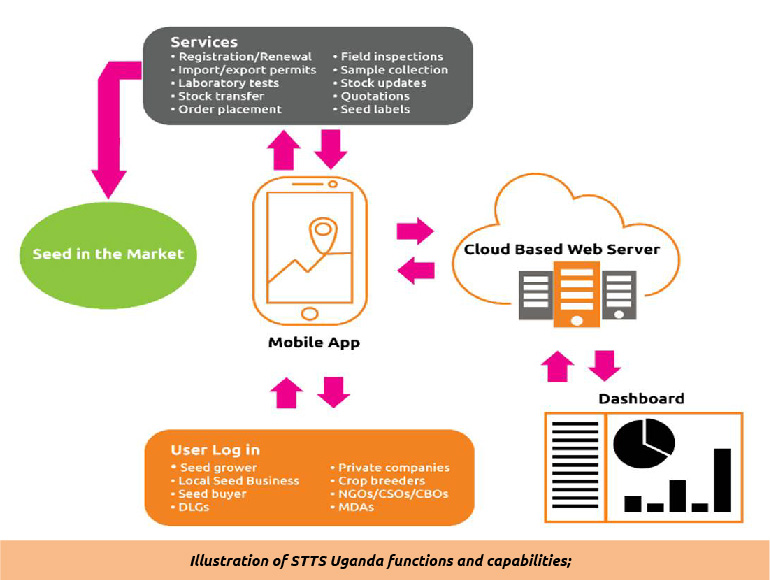
Integrated Seed and Sector Development (ISSD) Uganda through its Integrated Seed Sector Development Plus project (2017-2021), funded by Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs through its Embassy of the Kingdom of Netherlands in Uganda, supported Ministry of Agriculture Animal Industries and Fisheries (MAAIF) to develop an innovative digital system that can improve the regulation and access of quality seed for farmers. The system is called the National Seed tracking and tracing system (STTS). Keeping the quality of seed with desired traits along the seed value chain is still a big challenge in most developing countries. These has majorly been attributed to efficient human based processes which is cumbersome and prone to manipulations. The digital seed tracking and tracing systems (STTS) can provide a real time information on the movement of seed along the value chain to ensure strategic decision on quality related issues that can enable its technological benefits to be realized by the farmers. In addition the system provides real time data which can support policy reforms towards seed sector development and private sector investment.
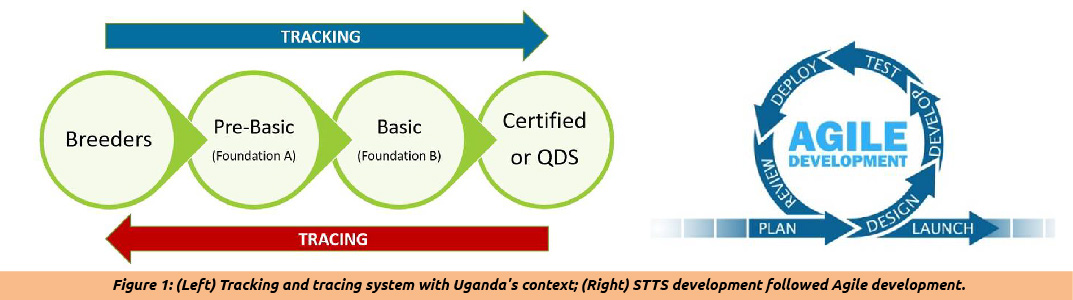
This involves recording the seed source, seed production of each seed field, seed lots at each seed producers, and seed packs with the use of unique seed field/lot identifiers with QRD code Generated at seed lotting level in seed testing laboratory. Tracking is particularly aimed at identity preservation and quality assurance, while tracing is aimed at solving problems faced by product non-conformance in customer experience or at any point along the seed production value chain.
Tracing is also required for product recall to the point of non-conformance with quality. Both tracking and tracing should be inherent in the country’s seed laws to complement the sector in the essential aspect of protecting seed users from counterfeit seeds. Access to affordable quality seed is the foundation of increasing agricultural production and productivity which are needed for food and nutrition security and income for farmers. To put the situation more graphically, by end of 2020, 69.2% (30.6million) Ugandans were food insecure with 21.7% with sever food insecurity (FAO, 2021; Nahalom et al., 2023). Improving access to quality seed with desired dietary composition, resilience for climate change adaption and high yields could contribute significantly in changing the food and nutrition insecurity in Uganda and the sub Saharan Africa at large. The digital STTS application offers a good approach towards achieving quality seed reaching the last mile through stamping out counterfeit seed in the market.
The development process started with a deeper analysis of the current seed sector regulatory system, business/work processes, decision making practices and information flow models. After the analysis, the requirements established are documented and a requirements specifications document was developed. The system requirements document will be validated through stakeholder engagement before the final requirements for each output (web portal and mobile app) can be signed off. Once requirements validated, the document will be shared with the software team for implementation and each output tested and validated. The web portal will then be deployed on the server to be used by administrators as the mobile application is being tested to enhance the feedback mechanism by the stakeholders and ensure its functionality. Users were trained before the module is deployed. During the system development, system user manuals and videos were also developed concurrently.